Publication
 HOME > Publications > Publication
HOME > Publications > Publication Enhancing the catalytic activity of Pt nanoparticles using poly sodium styrene sulfonate stabilized graphene support for methanol oxidation Hit : 800
Sundar Mayavan, Hyung-Sik Jang, Min-Jae Lee, Sun Hee Choi and Sung-Min Choi
1, 3489-3494 (2013)
 http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C2TA00619G
http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C2TA00619G
Abstract
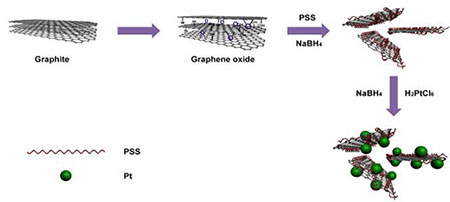
Pt NPs were in situ synthesised on poly(sodium styrene sulfonate) functionalized graphene supports (PSS–G) in aqueous solution. We investigate the reduction of graphene oxide, PSS adsorption on reduced graphene , and Pt NP functionalization by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS ), X-ray absorption fine structure studies (XAFS ), Raman spectroscopy , X-ray diffraction (XRD ), scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy . The as-prepared Pt on PSS–G sample (Pt–PSS–G) was used directly as a catalyst ink without further treatment. The use of PSS as a stabilizer prevents stacking of reduced graphene sheets, binds Pt NPs, and promotes mass transport of reaction species. The as-prepared Pt–PSS–G exhibits higher activity and stability for methanol oxidation reaction than Pt NPs supported on pristine graphene sheets (Pt–G). The higher activity is due to the presence of Pt NPs on the surface of the PSS–G support, which provides an integrated electron and mass transport pathway for every Pt NP. This work realizes both scalable and greener production of highly efficient catalysts , and would be valuable for practical applications of graphene based fuel cell catalysts .
순다 2013 450.jpg
1, 3489-3494 (2013)
 http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C2TA00619G
http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/C2TA00619G
Abstract

Pt NPs were in situ synthesised on poly(sodium styrene sulfonate) functionalized



